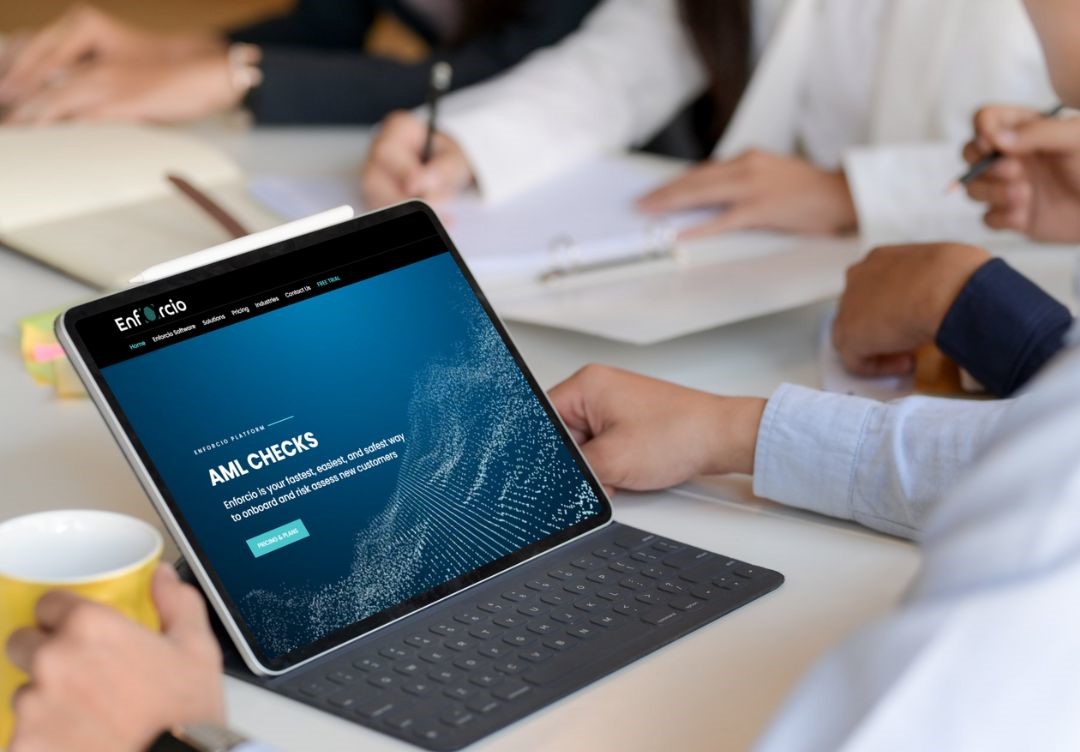
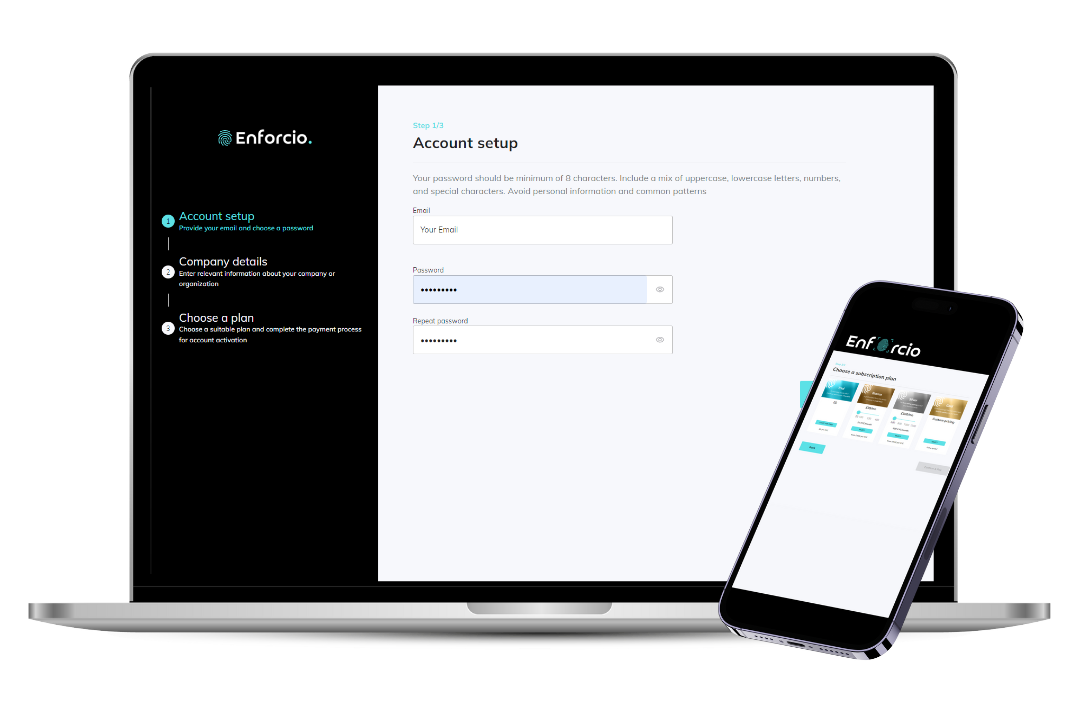
Enforcio Due Diligence solution offers a risk-based approach to KYC comliance that efficiently focuses resources on higher risk clients and ensures lifecycle compliance with KYC regulations
Enforcio software as Due Diligence solution UK
Enforcio Due Diligence solution with a pre-screening focus offers small businesses a systematic and efficient way to conduct initial assessments, enabling them to make well-informed decisions about whether to proceed with more extensive due diligence processes.
Customer Due Diligence, its purpose:
- Risk Mitigation: Identify and manage risks associated with customers.
- Compliance: Fulfil legal and regulatory requirements.
- Prevent Financial Crimes: Detect and prevent money laundering, terrorist financing, and other illicit activities.
Your benefits with the Due Diligence solution software focusing on pre-screening:
- Efficiency in Initial Checks
- Time and Resource Savings
- Early Identification of Risks
- Improved Decision-Making
- Enhanced Compliance
- Scalable Solutions
Automate your KYC & Onboarding process.
Get fast results with Enforcio, cost-efficient KYC software for ID verification, AML Compliance and Onboarding.
Onboard your clients in seconds!
Client onboarding made easy with Enforcio that automates verification, evaluates risk, and simplifies compliance with evolving regulations, such as AML and KYC checks.
Fight fraud during customer onboarding.
Prevent fraud before it can cause real harm to your business, and reduce the time to verify genuine customers.
Due Diligence solution
Protect your business when making new partnerships.
Uncover any risks to your firm that could arise from doing business with certain clients and prevent financial crime with Enforcio.
PRICING & PLANS 2025Due Diligence Solution UK

Bronze
from £99/month
A great solution for a one-person company or small team
3-400 KYC/month
from £0.62 per KYC

Silver
from £300/month
The best-selling package to suit your business needs
401-1200 KYC/month
from £0.38 per KYC
INDUSTRIESDue Diligence Solution UK
Designed by AML specialists for a wide range of small businesses, susceptible to the risk of being exploited for money laundering or illicit financial activities such as Real Estate Agencies, Legal and Accounting Firms.

Enforcio software helps automate, streamline and standardize Know Your Customer (KYC) process

Our software helps Accountants to make informed anti-money laundering decisions by automating processes and helping them to carry out due diligence

Our simple, cost-effective solution makes anti money laundering for estate agents easy
Information about CDD UK
What is Customer Due Diligence (CDD)?
Customer Due Diligence (CDD) is a process undertaken by businesses, especially in the financial and regulated sectors, to assess and understand their customers’ backgrounds, risks, and behaviors. The primary goal is to prevent financial crimes such as money laundering, terrorist financing, and fraud.
Is the Customer Due Diligence an integral part of the Know Your Customer (KYC) process?
Yes, Customer Due Diligence (CDD) is indeed an integral part of the Know Your Customer (KYC) process. KYC refers to the set of procedures and policies that businesses, particularly in the financial industry, implement to verify and identify their customers. The primary goal of KYC is to prevent illegal activities such as money laundering, fraud, and terrorist financing.
CDD specifically involves gathering and assessing information about a customer to understand their risk profile. This includes verifying the customer’s identity, understanding the nature of their business or financial transactions, and assessing the risk they pose in terms of money laundering or other illicit activities.
CDD helps institutions to have a comprehensive understanding of their customers, enabling them to make informed decisions, manage risks effectively, and comply with regulatory requirements. It involves ongoing monitoring of customer transactions and activities to ensure that the customer’s risk profile is up to date and that any unusual or suspicious behavior is promptly identified and reported.
Types of Customer Due Diligence UK
Customer Due Diligence can be categorized into three main types, each varying in intensity and depth of scrutiny:
- Standard Due Diligence:
This is the basic level of due diligence conducted for most customers.
It involves verifying the customer’s identity using reliable and independent sources, such as official identification documents (passport, driver’s license), utility bills, or financial statements.
The purpose is to establish the customer’s identity and assess the nature of the business relationship.
- Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD):
EDD is a more in-depth form of due diligence applied to customers posing a higher risk, often due to factors like the nature of the business, location, or the complexity of transactions.
It involves a more thorough examination of the customer’s background, source of funds, and the purpose of the transaction.
EDD may include additional checks on beneficial ownership, senior management, and other relevant parties.
It is typically applied to high-risk customers, such as politically exposed persons (PEPs) or customers involved in high-value transactions.
- Simplified Due Diligence (SDD):
SDD is applied to lower-risk customers or transactions, where the risk of money laundering or illicit activities is deemed to be low.
The level of scrutiny and documentation required for SDD is reduced compared to standard or enhanced due diligence.
This may involve relying on publicly available information or existing customer data, making the process less burdensome for low-risk scenarios.
The choice of the type of due diligence is often influenced by factors such as the customer’s risk profile, the type of business relationship, and regulatory requirements. Financial institutions and other entities subject to KYC regulations must tailor their due diligence procedures based on the perceived risk associated with each customer.
What are the key elements of Customer Due Diligence in UK?
Customer Due Diligence involves a comprehensive examination of a customer’s background, identity, and potential risks to prevent financial crimes. The key elements of CDD typically include:
- Customer Identification:
– Collection of basic identification information, including name, address, date of birth, and legal entity details for business customers.
– Verification of customer identity through official documents such as government-issued IDs, passports, or utility bills.
- Beneficial Ownership Verification:
– Identification and verification of individuals who ultimately own or control the customer, especially in the case of corporate entities or complex ownership structures.
– Understanding the ownership structure to assess the potential risks associated with beneficial owners.
- Understanding the Business Relationship:
– Determining the nature and purpose of the business relationship between the customer and the institution.
– Identifying the specific products or services being provided and the anticipated level of transactional activity.
- Risk Assessment:
– Evaluating the risk associated with the customer based on factors such as the nature of the business, geography, and the type and volume of transactions.
– Categorizing customers into low, medium, or high risk to determine the level of due diligence required (Standard Due Diligence or Enhanced Due Diligence).
- Source of Funds and Wealth:
– Understanding and verifying the source of the customer’s funds and wealth.
– Assessing the legitimacy of financial resources and ensuring they are not derived from illegal or unethical activities.
- Ongoing Monitoring:
– Implementing continuous monitoring of customer accounts and transactions to identify any unusual or suspicious activity.
– Regularly updating customer information to reflect any changes in risk profile or business activities.
- Politically Exposed Persons (PEP) Screening:
– Identifying whether the customer, or any beneficial owner, is a politically exposed person (PEP) who may be more susceptible to corruption or bribery.
– Applying enhanced scrutiny and monitoring for PEPs.
- Sanctions Screening:
– Checking customers against lists of sanctioned individuals, entities, or countries to ensure compliance with international sanctions regulations.
– Promptly identifying and reporting any matches to relevant authorities.
- Documentation and Record Keeping:
– Maintaining thorough records of the customer due diligence process, including documentation of identification efforts, risk assessments, and verification steps.
– Ensuring compliance with data protection and privacy regulations.
- Training and Awareness:
– Providing training to employees involved in the CDD process to enhance their understanding of regulatory requirements and risk factors.
– Ensuring ongoing awareness of evolving threats and compliance standards within the organization.
These elements collectively contribute to a robust Customer Due Diligence process, helping financial institutions and regulated entities to mitigate risks, comply with regulatory obligations, and maintain the integrity of their operations.
When is Customer Due Diligence required?
Customer Due Diligence (CDD) is required in various business contexts, particularly in the financial industry, to mitigate the risks associated with money laundering, fraud, and other illicit activities. The specific instances when CDD is typically required include:
- Account Opening:
When establishing a new business relationship or opening a new account for an individual or entity.
This is a fundamental step in the Know Your Customer (KYC) process.
- Financial Transactions:
Before executing high-value or complex financial transactions.
For transactions that are unusual or inconsistent with the customer’s established patterns.
- International Business Relationships:
When dealing with customers or entities in jurisdictions known for higher money laundering or terrorist financing risks.
Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) may be necessary in such cases.
- Politically Exposed Persons (PEPs):
When the customer is identified as a politically exposed person or has close associations with PEPs.
PEPs are individuals with prominent public functions, and their financial activities are subject to increased scrutiny.
- Changes in Customer Information:
Whenever there are significant changes in the customer’s information, such as a change in ownership, management, or business activities.
Ongoing monitoring helps detect and address such changes.
- Periodic Reviews:
Conducting periodic reviews of existing customer relationships to ensure that the customer information is up to date.
This helps in reassessing the risk associated with the customer over time.
- Risk-Based Approach:
As part of a risk-based approach, where the level of due diligence is determined by the perceived risk associated with the customer.
Higher-risk customers may require Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD), while lower-risk customers may undergo Simplified Due Diligence (SDD).
- Legal and Regulatory Requirements:
In accordance with legal and regulatory obligations imposed by national and international authorities.
Financial institutions and other entities are required to comply with AML and CTF regulations and may face penalties for non-compliance.
- Correspondent Banking:
For correspondent banking relationships, where one financial institution provides services to another.
Correspondent banks typically conduct thorough due diligence to manage risks associated with cross-border transactions.
The specific requirements and thresholds for CDD may vary by jurisdiction and industry, as different countries and sectors have their own regulations and standards. In many cases, financial institutions and regulated entities develop internal policies and procedures that align with regulatory expectations and industry best practices to ensure effective CDD processes.
Due Diligence softwares, types
Due diligence software refers to tools and platforms that facilitate the process of due diligence, which is the comprehensive assessment and investigation of a business or individual before entering into a transaction or agreement. Due diligence is commonly performed in mergers and acquisitions, investments, partnerships, and other business transactions to mitigate risks and ensure informed decision-making. Here are some types of due diligence software and their functionalities:
- Virtual Data Rooms (VDRs):
Purpose: Securely store and share confidential documents during due diligence processes.
Features: Document encryption, access controls, activity tracking, and audit trails.
- Compliance and Risk Assessment Software:
Purpose: Evaluate legal and regulatory compliance, identify potential risks.
Features: Automated risk assessments, compliance tracking, regulatory updates.
- Financial Due Diligence Software:
Purpose: Analyze financial statements, conduct financial modeling, and assess financial health.
Features: Financial analysis tools, forecasting, budgeting.
- Contract Management Software:
Purpose: Manage and review contracts to identify potential liabilities and obligations.
Features: Contract tracking, version control, search and analysis tools.
- Business Intelligence (BI) Tools:
Purpose: Analyze and visualize data to gain insights into the target company’s performance.
Features: Data visualization, analytics, dashboards.
- Cybersecurity Due Diligence Software:
Purpose: Assess the target’s cybersecurity posture and identify potential vulnerabilities.
Features: Vulnerability scanning, threat intelligence, risk assessments.
- Customer Due Diligence (CDD) Software:
Purpose: Verify the identity of customers and assess the risk of potential business relationships.
Features: Identity verification, risk profiling, compliance checks.
- Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Software:
Purpose: Evaluate the target’s performance in environmental, social, and governance aspects.
Features: ESG reporting, sustainability tracking, impact assessment.
- Due Diligence Automation Platforms:
Purpose: Streamline and automate the due diligence process for efficiency.
Features: Workflow automation, document indexing, collaboration tools.
When selecting due diligence software, consider the specific requirements of your due diligence process, the nature of the transaction, and the industry in which you operate. Additionally, ensure that the software complies with relevant legal and regulatory standards to maintain the integrity and confidentiality of the information being processed.